记Hadoop MapReduce入门学习
在之前的文章记hadoop伪分布式安装中,我们已经成功地安装了Hadoop,并且在文章在java中通过API读写hdfs入门学习中实现了通过java代码访问hdfs文件系统,接下来就进入到了MapReduce的学习。
网络上关于Hadoop的文章已经很多了,这里就不再具体介绍hadoop体系了。你只需要知道hadoop中包含hdfs和MapReduce两大子系统,hdfs仅是分布式文件系统,而MapReduce则是处理分布式文件的框架。即你只需要将你的需求转换为MapReduce的编程模型,然后提交运行即可,你不需要关心网络IO、并发锁、子任务划分等细节。
下面我们来具体看看如何将需求转为MapReduce编程模型,以及具体实现代码。
1. WordCount实现
之前学习Hadoop的时候,依稀记得它默认提供了一个WordCount程序用来验证系统是否成功安装,不知道现在还有没有。在本节中,我们来重新实现以下WordCount功能,WordCount功能指的是将一个文本文件中的单词进行统计计数。
和读写hdfs实验一样,需要做一些前置配置,具体可以查看文章在java中通过API读写hdfs入门学习
1.1 具体代码
前置工作完成后,接下来就可以编写具体代码了。
WordCount.java
package com.gavinzh.learn.hadoop;
import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import static java.util.function.Function.identity;
import static java.util.stream.Collectors.counting;
import static java.util.stream.Collectors.groupingBy;
/**
* 计数
*
* @author jiangmitiao
* @date 2021-02-17 13:17
*/
public class WordCount {
// 单词的格式描述
private static Pattern wordPattern = Pattern.compile("[a-zA-z]+");
// 解析一个字符串中的单词
public static List<String> parse(String str) {
Matcher matcher = wordPattern.matcher(str);
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
while (matcher.find()) {
result.add(matcher.group());
}
return result;
}
// Map步骤 解析出一行中的单词,对这些单词进行计数
public static class WordCountMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, LongWritable> {
@Override
protected void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
WordCount.parse(value.toString())
.stream()
.filter(StringUtils::isNotEmpty)
.filter(str -> str.length() > 1)
.collect(groupingBy(identity(), counting()))
.forEach((word, count) -> {
try {
context.write(new Text(word), new LongWritable(count));
} catch (IOException | InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
// Reduce步骤 将各个map子任务计数进行再次汇总,然后输出
public static class WordCountReducer extends Reducer<Text, LongWritable, Text, LongWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<LongWritable> values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
AtomicLong all = new AtomicLong(0L);
values.forEach(count -> all.addAndGet(count.get()));
context.write(key, new LongWritable(all.get()));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
if (args.length != 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: WordCount <in> <out>");
System.exit(2);
} else {
System.out.println("input: " + args[0]);
System.out.println("output: " + args[1]);
}
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
conf.set("fs.default.name", "hdfs://192.168.10.103:8999");
// 删除output
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
fs.delete(new Path(args[1]), true);
// 创建任务
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "word_count");
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
// 设置mapper和reducer
job.setMapperClass(WordCountMapper.class);
//job.setCombinerClass(WordCountReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(WordCountReducer.class);
// 设置 key value 格式
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
boolean result = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(result ? 0 : 1);
}
}
1.2 本机运行
上述代码可以在编辑器中直接运行,它将会读取hdfs中的文件,在本机做计算处理,然后将结果回写到hdfs。
需要注意的是需要设置一个全局变量用于表明用户身份:
HADOOP_USER_NAME=hadoop然后在填写程序参数:
这里的输入是之前下载的小说《杀死一只知更鸟》,输出到/test/word_count.txt
/test/to_kill_a_mockingbird.txt /test/word_count.txt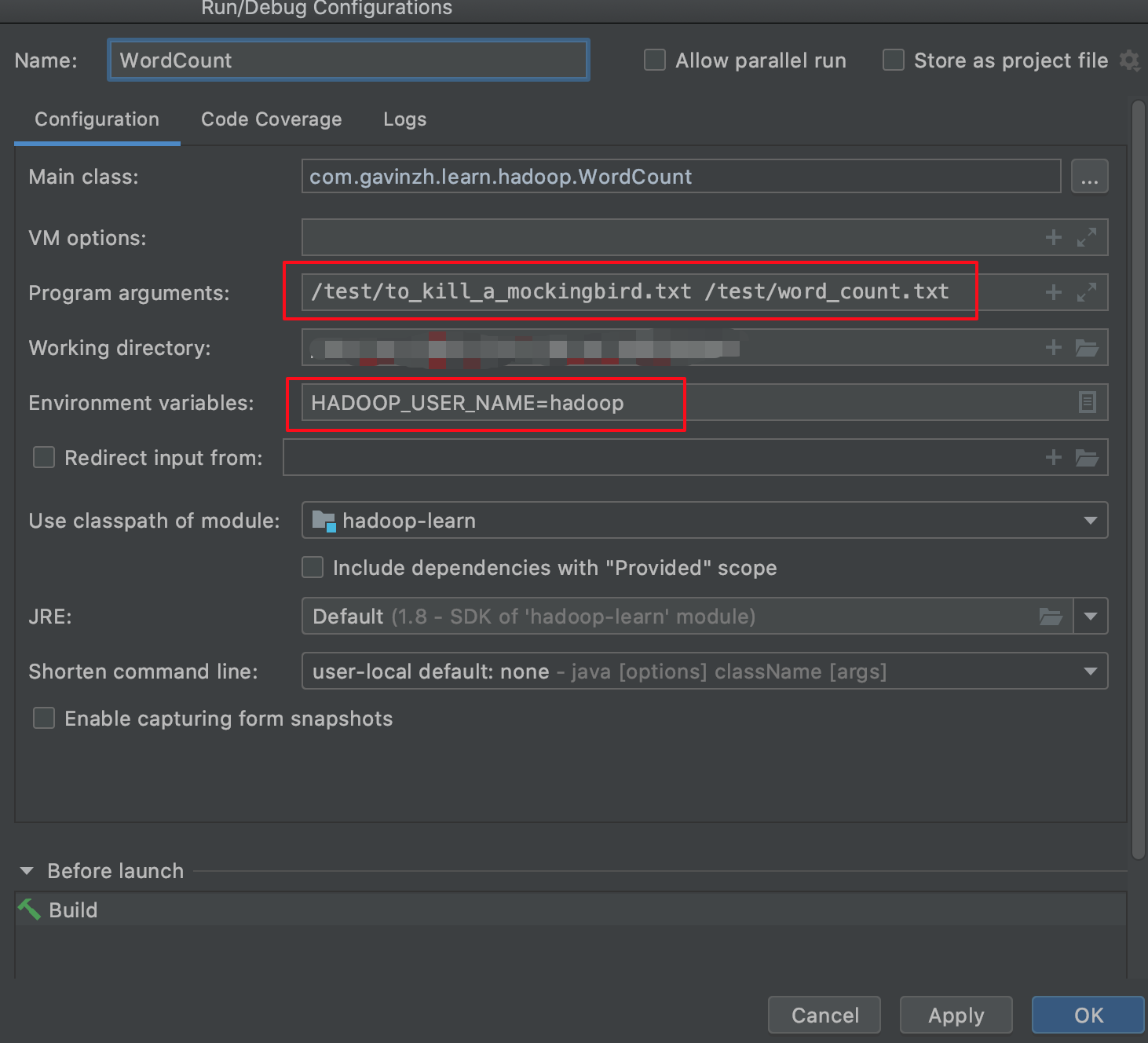
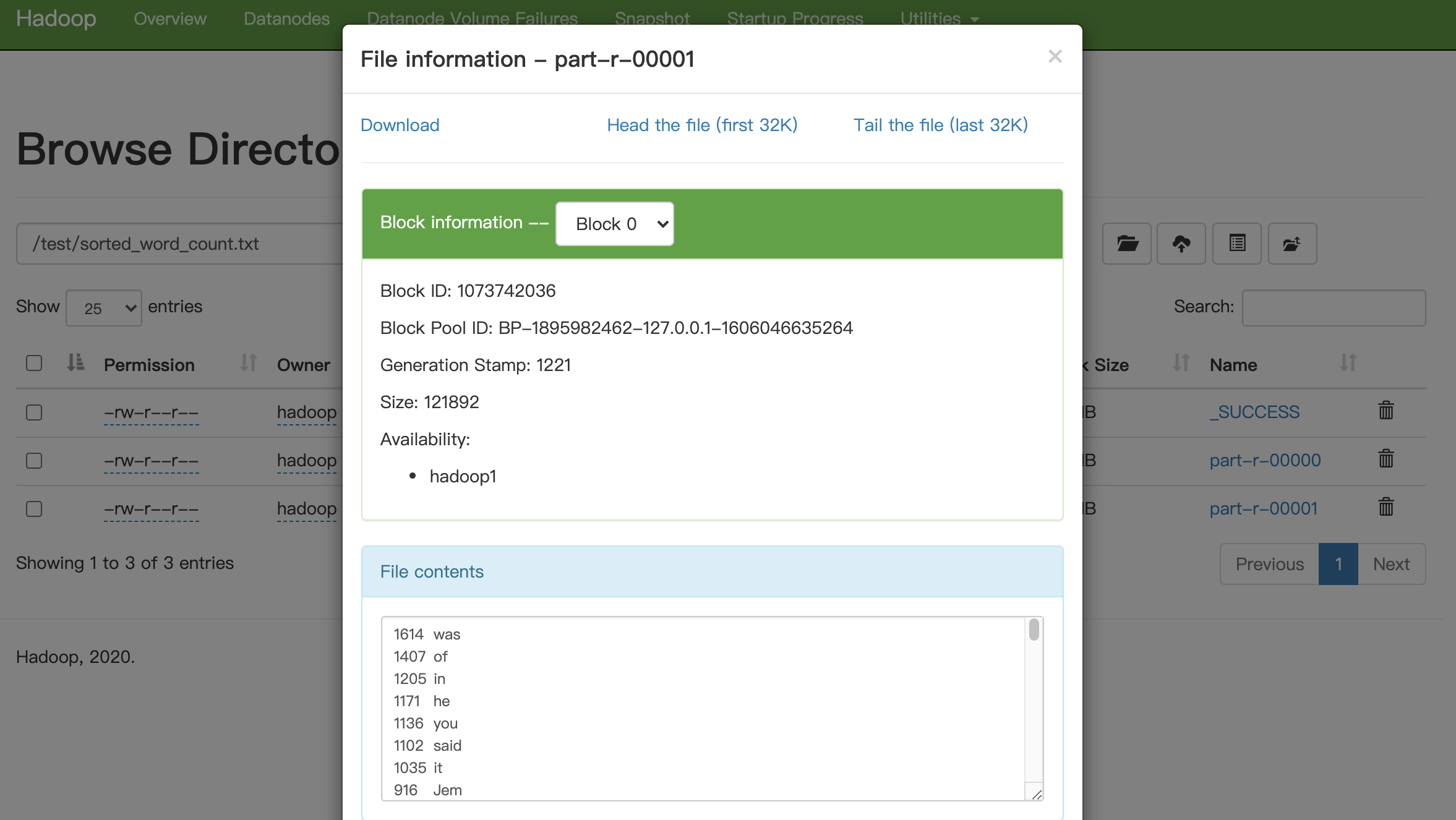
在本机运行完成后,在web管理界面查看文件信息,http://[dfs.http.address IP地址或域名]:50070/explorer.html#/。会得到以下结果:
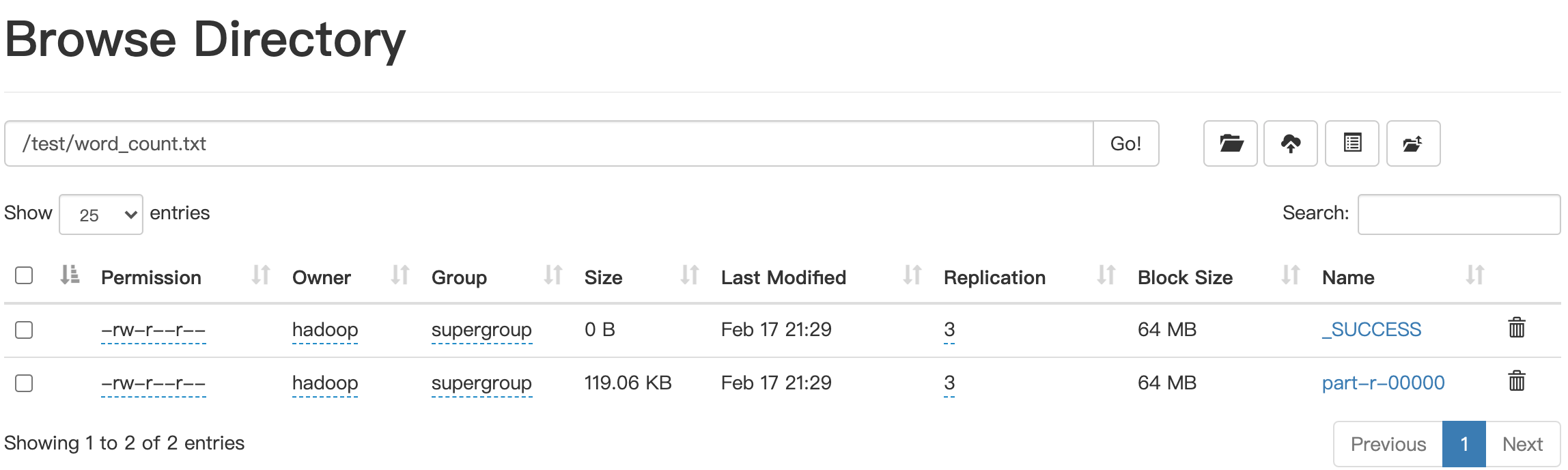
由于我们没有设置合并文件,之前设置的输出将会变成一个目录,在目录下包含一个成功标记空文件和数据文件part-r-00000,数据文件的多少和设置的reducer个数有关,后面我们会来演示多个reducer的情况。
点击文件名,可以查看文件具体信息: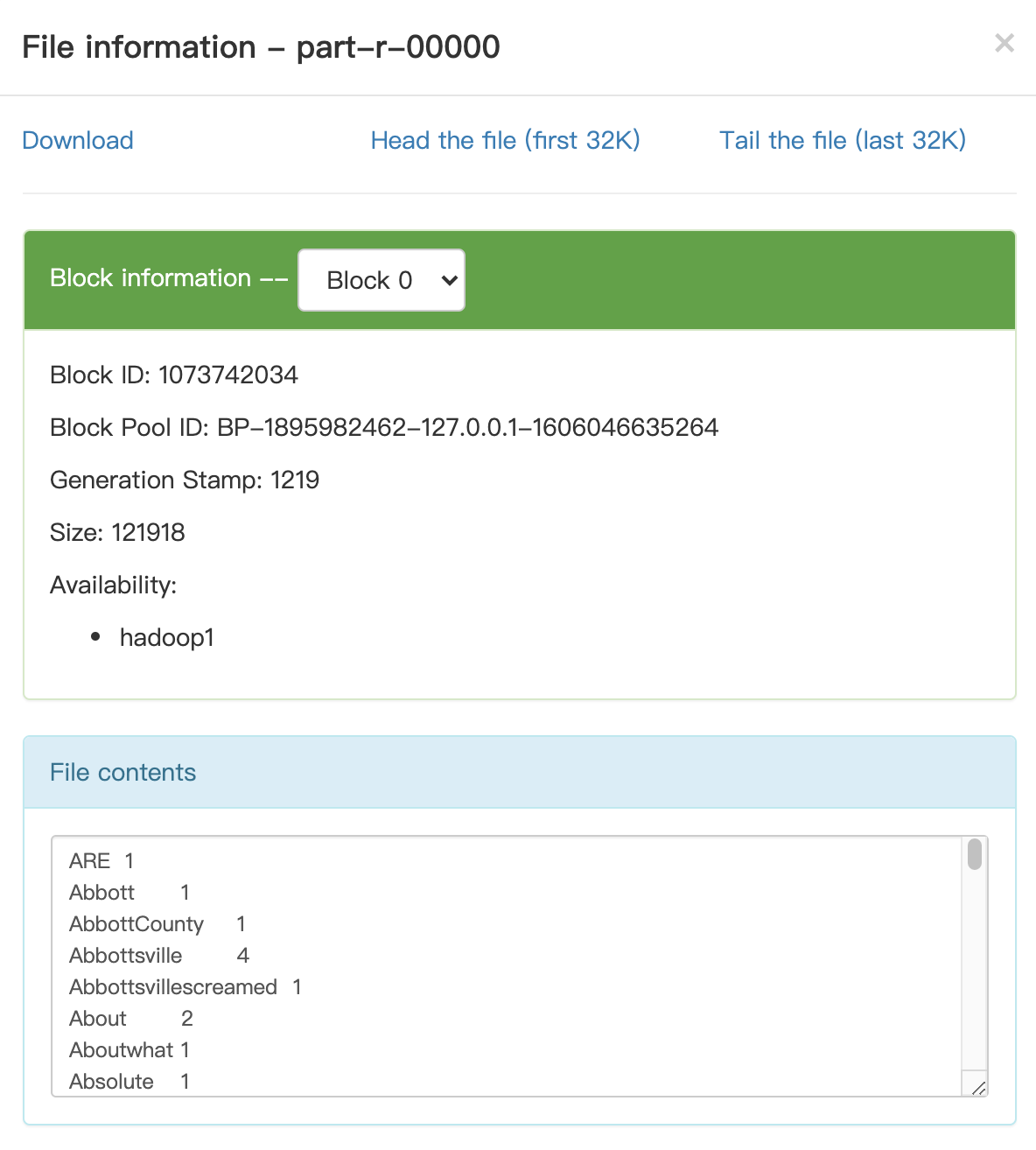
大家可以注意下,该文件内容是有序的,实际上在一个reducer子任务中,reducer会按照key进行排序。
1.3 提交yarn运行
在本机运行没有问题后,可以将任务提交到yarn中运行,它会分发任务到NodeManager管理的机器。
具体操作如下:
1.3.1 程序打包
由于我们的程序中可能会包含第三方jar包,所以需要将使用到的jar包进行统一打包,可以参照之前的文章Maven打包之maven-shade-plugin
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1.1</version>
<configuration>
<!-- put your configurations here -->
<!--只包含该项目代码中用到的jar,在父项目中引入了,但在当前模块中没有用到就会被删掉-->
<minimizeJar>true</minimizeJar>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<configuration>
<!--创建一个你自己的标识符,位置在原有名称之后-->
<shadedArtifactAttached>true</shadedArtifactAttached>
<shadedClassifierName>shade</shadedClassifierName>
<!--在打包过程中对文件做一些处理工作-->
<transformers>
<!--在META-INF/MANIFEST.MF文件中添加key: value 可以设置Main方法-->
<transformer
implementation="org.apache.maven.plugins.shade.resource.ManifestResourceTransformer">
<manifestEntries>
<mainClass>com.gavinzh.learn.hadoop.WordCount</mainClass>
<Build-Number>123</Build-Number>
<Built-By>your name</Built-By>
<X-Compile-Source-JDK>1.7</X-Compile-Source-JDK>
<X-Compile-Target-JDK>1.7</X-Compile-Target-JDK>
</manifestEntries>
</transformer>
</transformers>
</configuration>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>shade</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>1.3.2 提交程序
打完包后,使用scp命令将本地的包上传到hadoop机器上。
scp -r hadoop-learn-1.0-SNAPSHOT-shade.jar root@192.168.10.103:/home/hadoop然后使用hadoop命令提交运行:
hadoop jar hadoop-learn-1.0-SNAPSHOT-shade.jar /test/to_kill_a_mockingbird.txt /test/word_count.txt1.3.3 查看任务运行情况
当任务提交运行后,可以在之前配置好的 http://[yarn.resourcemanager.webapp.address IP地址或域名]:8088/cluster中查看运行情况了。
1.3.4 注意事项和小结
需要注意一点,提交任务后可能会出现hadoop相关类找不到,这是因为没有在hadoop的配置文件中增加相关classpath。
首先使用hadoop classpath命令得到classpath,然后将classpath配置到yarn-site.xml中。
<property>
<name>yarn.application.classpath</name>
<value>
/usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop:/usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/common/lib/*:/usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/common/*:/usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/hdfs:/usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/hdfs/lib/*:/usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/hdfs/*:/usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/mapreduce/*:/usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/yarn:/usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/yarn/lib/*:/usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/yarn/*
</value>
</property>2. WordCount排序实现
在第一节中,我们实现了WordCount功能,并且得到了每个单词的统计计数,但这些计数没有按照从大到小进行排序,不方便我们分析。接下来,我们在上一节的基础上,对处理好的单词计数进行排序。
由于reducer默认会按照key进行排序,那么我们可以将统计计数作为key进行map,但是由于Hadoop自带的LongWritable默认是从小到大排序的,因此我们需要实现一个能从大到小的key类型。其次,由于reducer子任务之间不保证有序,所以需要设计一个分区器,将数据按照统计计数的大小发送到不同的子任务中。
下面是具体代码:
SortedWordCount.java
package com.gavinzh.learn.hadoop;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author jiangmitiao
* @date 2021-02-17 15:15
*/
public class SortedWordCount {
// 定义一个bean 按照数字大小进行倒排
public static class SortedLongWritable extends LongWritable {
public SortedLongWritable() {
}
public SortedLongWritable(long value) {
super(value);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(LongWritable o) {
long thisValue = this.get();
long thatValue = o.get();
return (thisValue > thatValue ? -1 : (thisValue == thatValue ? 0 : 1));
}
}
// 自定义分区器 根据数字大小决定处理数据的reducer 3500是拍脑袋定的,实际上应该采样
public static class SortedPartitioner extends Partitioner<SortedLongWritable, Text> {
@Override
public int getPartition(SortedLongWritable sortedLongWritable, Text text, int numPartitions) {
long value = sortedLongWritable.get();
long bound = (3500L / numPartitions) + 1;
for (int i = 0; i < numPartitions; i++) {
if (value >= bound * i && value < bound * (i + 1)) {
return numPartitions - i - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
// 按照单词统计计数进行map
public static class SortedWordCountMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, SortedLongWritable, Text> {
@Override
protected void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] str = value.toString().split("\t");
context.write(new SortedLongWritable(Long.parseLong(str[1])), new Text(str[0]));
}
}
// 处理的数据为统计计数和对应的单词列表 将每个单词和计数写入到context中
public static class SortedWordCountReducer extends Reducer<SortedLongWritable, Text, LongWritable, Text> {
@Override
protected void reduce(SortedLongWritable key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
values.forEach(value -> {
try {
context.write(key, value);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
if (args.length != 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: SortedWordCount <in> <out>");
System.exit(2);
} else {
System.out.println("input: " + args[0]);
System.out.println("output: " + args[1]);
}
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
conf.set("fs.default.name", "hdfs://192.168.10.103:8999");
// 删除output
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
fs.delete(new Path(args[1]), true);
// 创建任务
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "sorted_word_count");
job.setJarByClass(SortedWordCount.class);
// 设置mapper和reducer
job.setMapperClass(SortedWordCountMapper.class);
//job.setCombinerClass(WordCountReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(SortedWordCountReducer.class);
// 设置分区器和reducer任务数量
job.setPartitionerClass(SortedPartitioner.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks(2);
// 设置 key value 格式
job.setOutputKeyClass(SortedLongWritable.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
boolean result = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(result ? 0 : 1);
}
}
打包时注意:将插件配置中的mainClass改为SortedWordCount。
提交任务:
hadoop jar hadoop-learn-1.0-SNAPSHOT-shade.jar /test/word_count.txt/part-r-00000 /test/sorted_word_count.txt查看数据,part0:
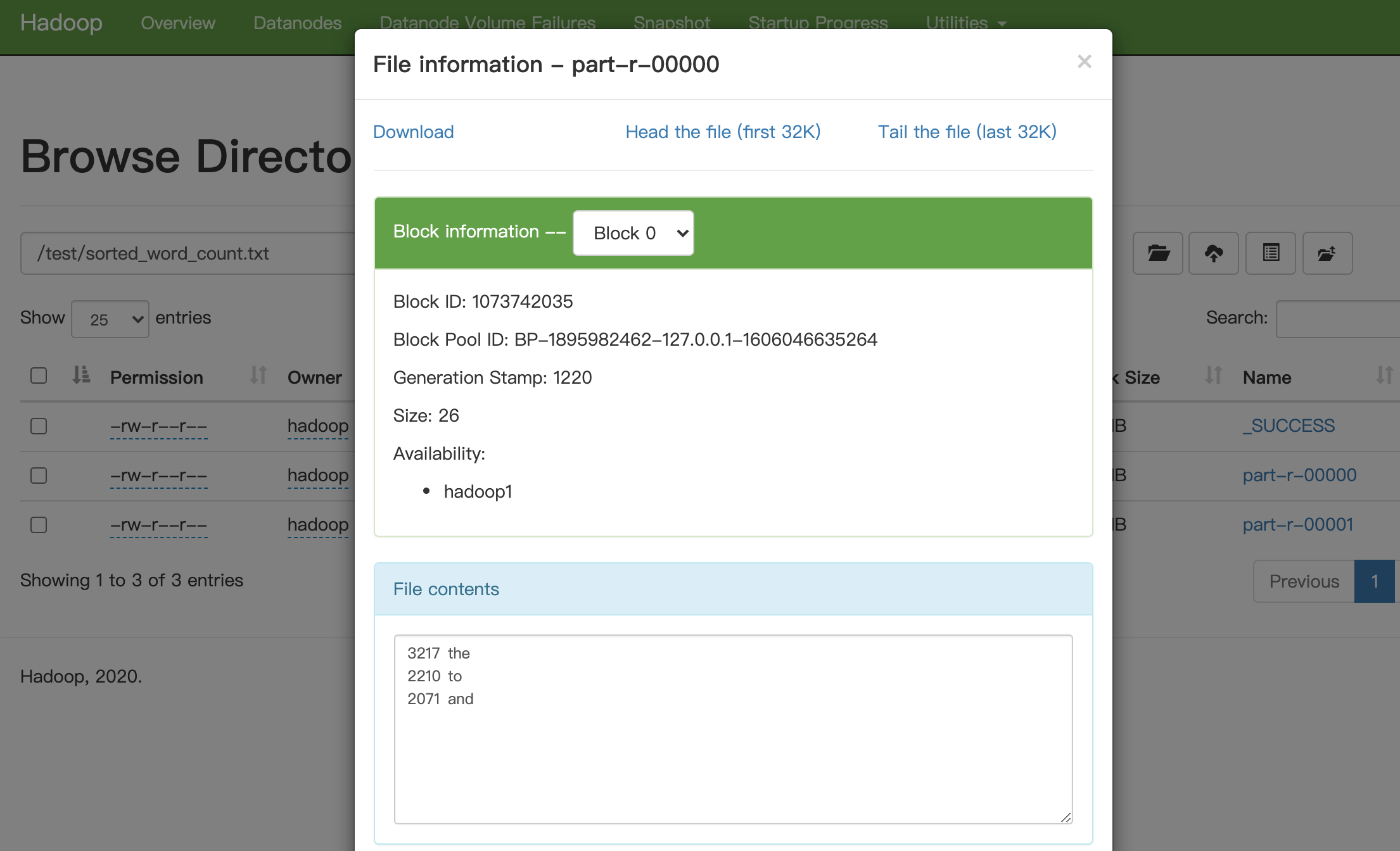
part1:
3. LeftJoin实现
前两节我们演示了MapReduce如何处理单个文件,接下来我们来看看MapReduce如何处理多个文件关联。
3.1 定义数据
我们需要先定义两个表,他们的内容是这样的:
table_a.txt
编号,姓名,父亲姓名
1,小明,大明
2,小红,大红
3,大明,大大明
4,大红,大大红table_b.txt
编号,年龄
1,10
2,11
3,34
4,35定义好这两个表后,将这两个表上传到hdfs中。
hadoop fs -put table_a.txt /test/
hadoop fs -put table_b.txt /test/3.2 代码实现
由于MapReduce需要一次读取两个文件,并且这两个文件的内容都不太一样,那么需要定义一个统一的结构体用于数据传输,下面我们定义了一个类TableLine用于保存数据。
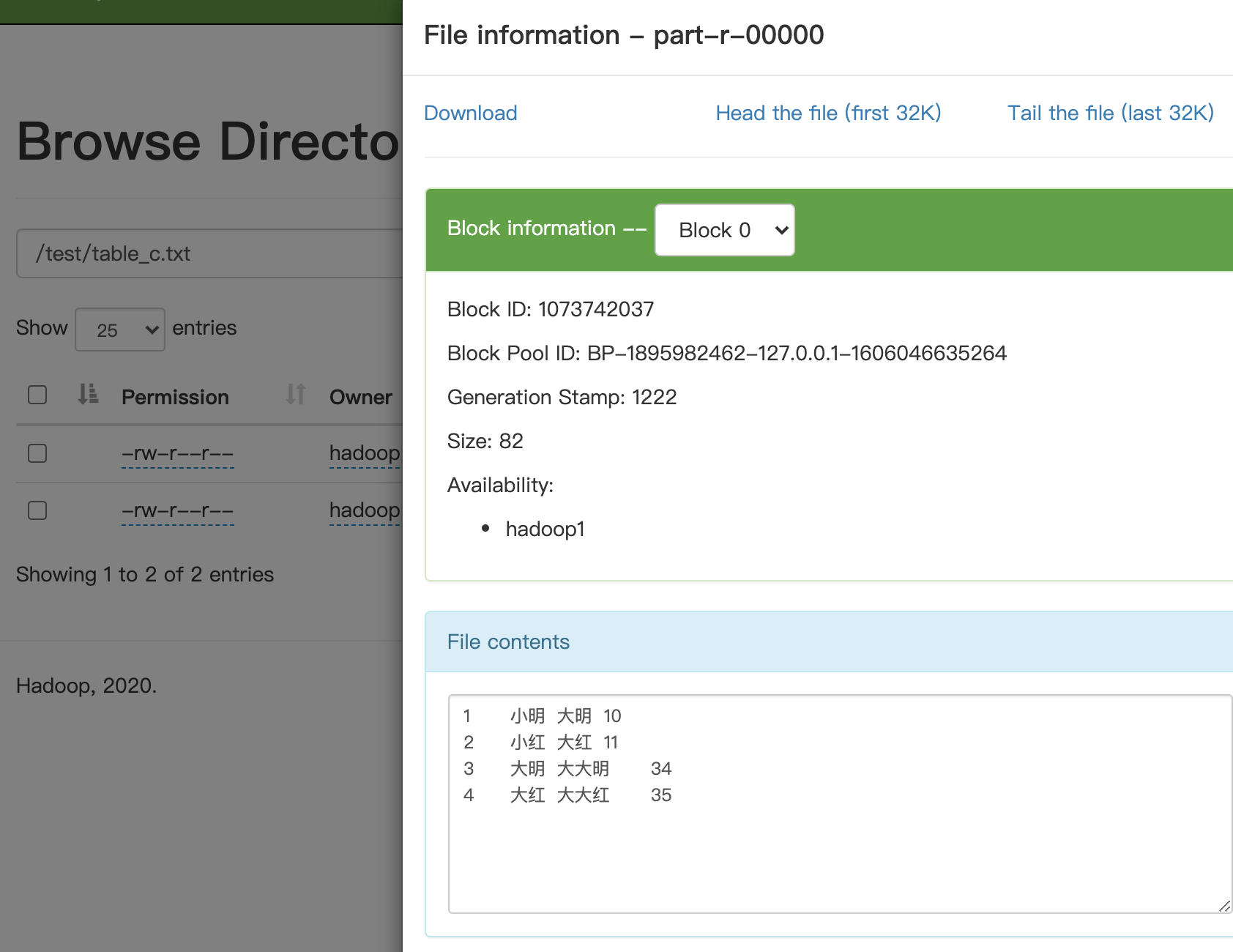
a和b两个表由于都有统一的id,所以可以在map阶段用id将这两个表的数据关联起来,在reduce阶段,就会得到一个key对应一个到两个value,value的类型为TableLine。分别获取a和b的TableLine,将他们整合然后写入到context中,即完成了关系处理。
具体代码如下:
TableLine.java
package com.gavinzh.learn.hadoop.relation;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import static java.lang.String.format;
/**
* @author jiangmitiao
* @date 2021-02-17 18:53
*/
public class TableLine extends Text {
public TableLine() {
}
public TableLine(String string) {
super(string);
}
public TableLine(String tableName, Long id, List<String> attrs) {
super(format("%s,%s,%s", tableName, id, String.join(",", attrs)));
}
public String getTableName() {
return super.toString().split(",")[0];
}
public Long getId() {
return Long.parseLong(super.toString().split(",")[1]);
}
public List<String> getAttrs() {
String[] values = super.toString().split(",");
if (values.length<=2){
return Arrays.asList();
}
return Arrays.asList(Arrays.copyOfRange(values, 2, values.length));
}
}LeftJoin.java
package com.gavinzh.learn.hadoop.relation;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import static java.lang.String.join;
/**
* @author jiangmitiao
* @date 2021-02-17 18:47
*/
public class LeftJoin {
public static class LeftJoinMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, LongWritable, TableLine> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
FileSplit inputSplit = (FileSplit)context.getInputSplit();
String filename = inputSplit.getPath().getName();
String[] values = value.toString().split(",");
long id = Long.parseLong(values[0]);
values = Arrays.copyOfRange(values, 1, values.length);
context.write(new LongWritable(id), new TableLine(filename, id, Arrays.asList(values)));
}
}
public static class LeftJoinReducer extends Reducer<LongWritable, TableLine, LongWritable, Text> {
@Override
protected void reduce(LongWritable key, Iterable<TableLine> values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
final TableLine left = new TableLine();
final TableLine right = new TableLine();
for (TableLine value : values) {
if (value.getTableName().startsWith("table_a")) {
left.set(value.toString());
}
if (value.getTableName().startsWith("table_b")) {
right.set(value.toString());
}
}
if (left.toString().equals("")) {
return;
}
if (right.toString().equals("")) {
context.write(key, new Text(join("\t", left.getAttrs())));
return;
}
Text all = new Text(join("\t", left.getAttrs()) + "\t" + join("\t", right.getAttrs()));
context.write(key, all);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
if (args.length != 3) {
System.err.println("Usage: LeftJoin <in1> <in2> <out>");
System.exit(3);
} else {
System.out.println("input1: " + args[0]);
System.out.println("input2: " + args[1]);
System.out.println("output: " + args[2]);
}
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
conf.set("fs.default.name", "hdfs://192.168.10.103:8999");
// 删除output
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
fs.delete(new Path(args[2]), true);
// 创建任务
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "left_join");
job.setJarByClass(LeftJoin.class);
// 设置mapper和reducer
job.setMapperClass(LeftJoinMapper.class);
//job.setCombinerClass(WordCountReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(LeftJoinReducer.class);
// 设置 key value 格式
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(LongWritable.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(TableLine.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(LongWritable.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[2]));
boolean result = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(result ? 0 : 1);
}
}
提交运行:
hadoop jar hadoop-learn-1.0-SNAPSHOT-sorted.jar /test/table_a.txt /test/table_b.txt /test/table_c.txt运行结果:
4 自关联功能实现
基于第三节,假设我们有个需求需要得到每个人父亲的父亲,意思就是找到小明的爷爷大大明,那么该如何实现呢?
我们可以这么来理解,在一行数据中,可以找到一个人的父亲,也可以找到一个人的儿子,例如在小明这行数据中,可以得到小明的父亲是大明,也可以得到大明的儿子是小明。那么可以在map阶段,将一行数据写两遍到context中,第一遍以儿子为key,value为son,name和furtherName,第二遍以父亲为key,value为further,name和furtherName。
在reduce阶段,如果一个key有两个value,则说明能找到它的son和further,也就是说能找到一个son的further的futher。
代码实现如下:
SelfJoin.java
package com.gavinzh.learn.hadoop.relation;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author jiangmitiao
* @date 2021-02-17 18:47
*/
public class SelfJoin {
public static class SelfJoinMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, TableLine> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
FileSplit inputSplit = (FileSplit)context.getInputSplit();
String filename = inputSplit.getPath().getName();
String[] values = value.toString().split(",");
long id = Long.parseLong(values[0]);
String son = values[1];
String further = values[2];
context.write(new Text(further), new TableLine("son", id, Arrays.asList(son, further)));
context.write(new Text(son), new TableLine("further", id, Arrays.asList(son, further)));
}
}
public static class SelfJoinReducer extends Reducer<Text, TableLine, Text, Text> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<TableLine> values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
final TableLine left = new TableLine();
final TableLine right = new TableLine();
for (TableLine value : values) {
if (value.getTableName().startsWith("son")) {
left.set(value.toString());
}
if (value.getTableName().startsWith("further")) {
right.set(value.toString());
}
}
if (left.toString().equals("")) {
return;
}
if (right.toString().equals("")) {
return;
}
Text all = new Text(left.getAttrs().get(0) + "\t" + right.getAttrs().get(1));
context.write(key, all);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
if (args.length != 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: SelfJoin <in> <out>");
System.exit(2);
} else {
System.out.println("input: " + args[0]);
System.out.println("output: " + args[1]);
}
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
conf.set("fs.default.name", "hdfs://192.168.10.103:8999");
// 删除output
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
fs.delete(new Path(args[1]), true);
// 创建任务
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "self_join");
job.setJarByClass(SelfJoin.class);
// 设置mapper和reducer
job.setMapperClass(SelfJoinMapper.class);
//job.setCombinerClass(WordCountReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(SelfJoinReducer.class);
// 设置 key value 格式
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(TableLine.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
boolean result = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(result ? 0 : 1);
}
}
提交任务:
hadoop jar hadoop-learn-1.0-SNAPSHOT-sorted.jar /test/table_a.txt /test/table_d.txt运行结果: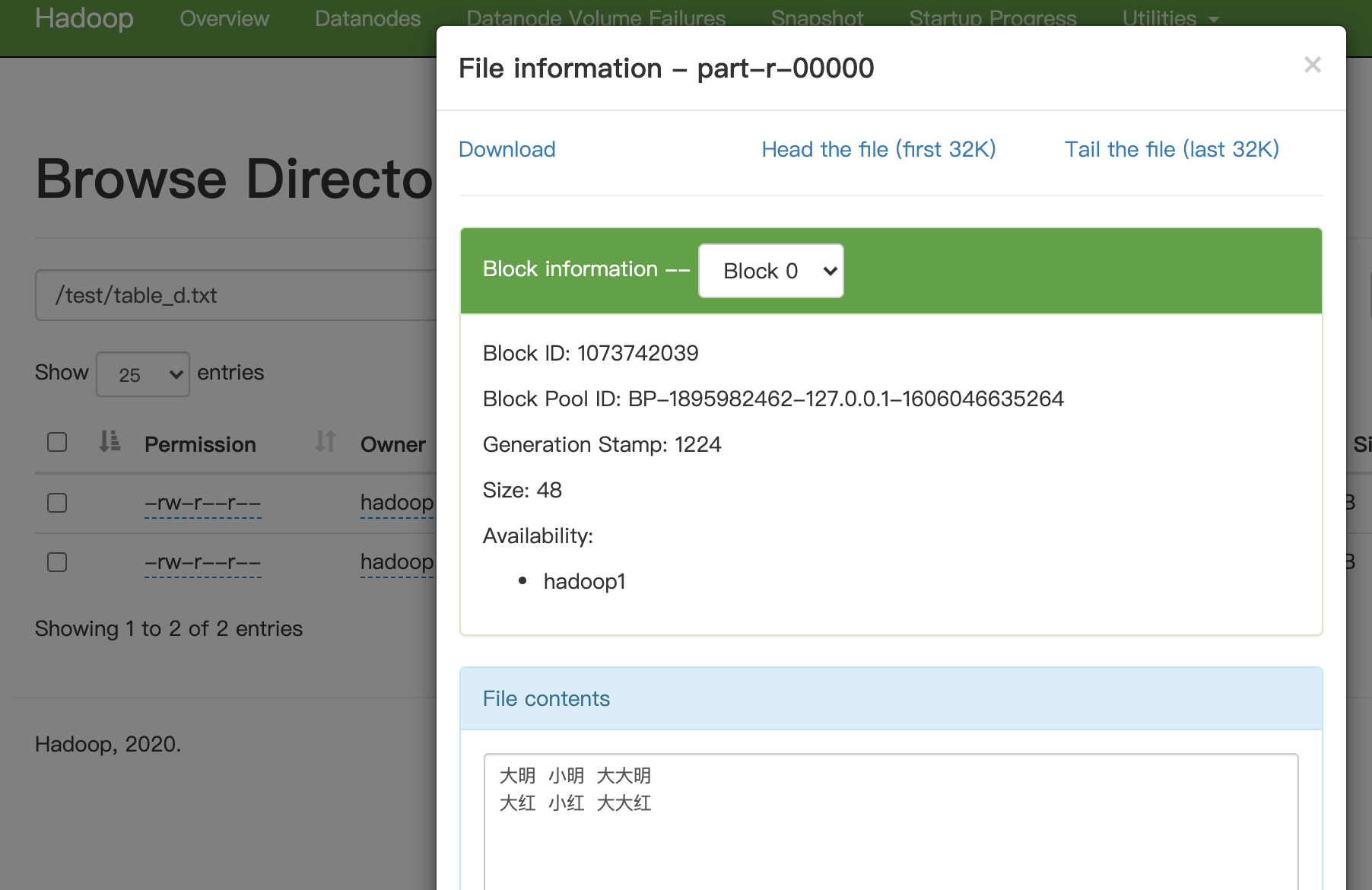
5. 小结
在上边四个小结中,我们演示了一些实际需求的MapReduce实现。可以看出,使用一个或多个MapReduce任务可以实现很多数据统计功能,网上也有人总结了常用的统计实现思路。但我们也能看出,它和我们日常数据分析所使用的SQL语言逻辑一点都不像,为了完成一个需求,可能需要编写多个MapReduce任务,这些任务间还需要指定顺序,对于大部分人而言,写MapReduce任务就是很困难的事情。
基于这种情况,雅虎和脸书分别开源了类SQL数据分析工具Pig和Hive,这两个工具可以将类SQL编译为MapReduce任务,这两个工具的出现大大降低了大数据编程门槛,开发者不需要直面MapReduce,只需要写写他们熟悉的SQL,就可以完成数据分析工作。
看来我就只有使用开箱即用产品的命了
目前直接使用MapReduce的人应该不多了,都是用hive、odps之类的上层产品。学习MapReduce实际上只是了解这些上层产品底层的运行逻辑。
看来我就只有使用开箱即用产品的命了