Spring扩展点总结
spring中bean的扩展点
经历了一系列复杂的spring应用后,你的项目可能已经用上注解,也用上了xxx.properties,你对这神奇的用法感到欣喜,但你不知道他是怎么被实现的,现在就让我们来揭开这些神秘的面纱。
BeanDefinition与BeanFactory扩展
在Spring生成bean的过程这篇文章中,我们了解了spring在生成bean前会先生成bean的定义,然后注册到BeanFactory中,再之后才能生成bean。那么对于从xml配置好的BeanDefinition,如果想要增加删除修改该怎么办呢?
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口继承了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口随后我们也会讲到这个接口。
接口描述
/**
* Extension to the standard {@link BeanFactoryPostProcessor} SPI, allowing for
* the registration of further bean definitions <i>before</i> regular
* BeanFactoryPostProcessor detection kicks in. In particular,
* BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor may register further bean definitions
* which in turn define BeanFactoryPostProcessor instances.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.0.1
* @see org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
*/
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean definition registry after its
* standard initialization. All regular bean definitions will have been loaded,
* but no beans will have been instantiated yet. This allows for adding further
* bean definitions before the next post-processing phase kicks in.
* @param registry the bean definition registry used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException;
}这个接口扩展了标准的BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口,允许在普通的BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口实现类执行之前注册更多的BeanDefinition。特别地是,BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor可以注册BeanFactoryPostProcessor的BeanDefinition。
postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法可以修改在BeanDefinitionRegistry接口实现类中注册的任意BeanDefinition,也可以增加和删除BeanDefinition。原因是这个方法执行前所有常规的BeanDefinition已经被加载到BeanDefinitionRegistry接口实现类中,但还没有bean被实例化。
接口应用
我们仅仅需要写一个类实现接口,然后将这个类配置到spring的xml配置中。以下是我写的一个简单的实现类:
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor;
public class DefaultBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
logger.info("BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法,在这里可以增加修改删除bean的定义");
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
logger.info("BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法,在这里可以对beanFactory做一些操作");
}
}实际上,Mybatis中org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer就实现了该方法,在只有接口没有实现类的情况下找到接口方法与sql之间的联系从而生成BeanDefinition并注册。而Spring的org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor也是用来将注解@Configuration中的相关生成bean的方法所对应的BeanDefinition进行注册。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口
BeanFactory生成后,如果想对BeanFactory进行一些处理,该怎么办呢?BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口就是用来处理BeanFactory的。
接口描述
/**
* Allows for custom modification of an application context's bean definitions,
* adapting the bean property values of the context's underlying bean factory.
*
* <p>Application contexts can auto-detect BeanFactoryPostProcessor beans in
* their bean definitions and apply them before any other beans get created.
*
* <p>Useful for custom config files targeted at system administrators that
* override bean properties configured in the application context.
*
* <p>See PropertyResourceConfigurer and its concrete implementations
* for out-of-the-box solutions that address such configuration needs.
*
* <p>A BeanFactoryPostProcessor may interact with and modify bean
* definitions, but never bean instances. Doing so may cause premature bean
* instantiation, violating the container and causing unintended side-effects.
* If bean instance interaction is required, consider implementing
* {@link BeanPostProcessor} instead.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 06.07.2003
* @see BeanPostProcessor
* @see PropertyResourceConfigurer
*/
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard
* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans
* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for overriding or adding
* properties even to eager-initializing beans.
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}这个接口允许自定义修改应用程序上下文的BeanDefinition,调整上下文的BeanFactory的bean属性值。应用程序上下文可以在BeanFactory的BeanDefinition中自动检测BeanFactoryPostProcessor bean,并在创建任何其他bean之前应用它们。对于定位于系统管理员的自定义配置文件非常有用,它们将覆盖应用程序上下文中配置的bean属性。请参阅PropertyResourceConfigurer及其具体实现,了解解决此类配置需求的开箱即用解决方案。BeanFactoryPostProcessor可能与bean定义交互并修改,但永远不应该将bean实例化。 这样做可能会导致过早的bean实例化,违反容器执行顺序并导致意想不到的副作用。如果需要bean实例交互,请考虑实现BeanPostProcessor接口。
postProcessBeanFactory方法在BeanFactory初始化后,所有的bean定义都被加载,但是没有bean会被实例化时,允许重写或添加属性。
接口应用
与DefaultBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口一样,实现并配置到spring的xml配置中即可。
最常用的一个应用就是org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer,BeanDefinition生成后,可能某些参数是${key},这个实现类就是把前边这种参数转换成xxx.properties中key所对应的值。
Bean实例化中的扩展
前一小节关注的是BeanDefinition和BeanFactory,那么在bean的实例化过程中会调用一些特定的接口实现类,这些接口都有哪些?
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口
接口描述
/**
* Subinterface of {@link BeanPostProcessor} that adds a before-instantiation callback,
* and a callback after instantiation but before explicit properties are set or
* autowiring occurs.
*
* <p>Typically used to suppress default instantiation for specific target beans,
* for example to create proxies with special TargetSources (pooling targets,
* lazily initializing targets, etc), or to implement additional injection strategies
* such as field injection.
*
* <p><b>NOTE:</b> This interface is a special purpose interface, mainly for
* internal use within the framework. It is recommended to implement the plain
* {@link BeanPostProcessor} interface as far as possible, or to derive from
* {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter} in order to be shielded
* from extensions to this interface.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Rod Johnson
* @since 1.2
* @see org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#setCustomTargetSourceCreators
* @see org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.target.LazyInitTargetSourceCreator
*/
public interface InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor <i>before the target bean gets instantiated</i>.
* The returned bean object may be a proxy to use instead of the target bean,
* effectively suppressing default instantiation of the target bean.
* <p>If a non-null object is returned by this method, the bean creation process
* will be short-circuited. The only further processing applied is the
* {@link #postProcessAfterInitialization} callback from the configured
* {@link BeanPostProcessor BeanPostProcessors}.
* <p>This callback will only be applied to bean definitions with a bean class.
* In particular, it will not be applied to beans with a "factory-method".
* <p>Post-processors may implement the extended
* {@link SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor} interface in order
* to predict the type of the bean object that they are going to return here.
* @param beanClass the class of the bean to be instantiated
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean object to expose instead of a default instance of the target bean,
* or {@code null} to proceed with default instantiation
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinition#hasBeanClass
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinition#getFactoryMethodName
*/
Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException;
/**
* Perform operations after the bean has been instantiated, via a constructor or factory method,
* but before Spring property population (from explicit properties or autowiring) occurs.
* <p>This is the ideal callback for performing field injection on the given bean instance.
* See Spring's own {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor}
* for a typical example.
* @param bean the bean instance created, with properties not having been set yet
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return {@code true} if properties should be set on the bean; {@code false}
* if property population should be skipped. Normal implementations should return {@code true}.
* Returning {@code false} will also prevent any subsequent InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
* instances being invoked on this bean instance.
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
/**
* Post-process the given property values before the factory applies them
* to the given bean. Allows for checking whether all dependencies have been
* satisfied, for example based on a "Required" annotation on bean property setters.
* <p>Also allows for replacing the property values to apply, typically through
* creating a new MutablePropertyValues instance based on the original PropertyValues,
* adding or removing specific values.
* @param pvs the property values that the factory is about to apply (never {@code null})
* @param pds the relevant property descriptors for the target bean (with ignored
* dependency types - which the factory handles specifically - already filtered out)
* @param bean the bean instance created, but whose properties have not yet been set
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the actual property values to apply to the given bean
* (can be the passed-in PropertyValues instance), or {@code null}
* to skip property population
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.MutablePropertyValues
*/
PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(
PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException;
}这个接口是BeanPostProcessor的子接口,用于在实例化之后,但在设置显式属性或自动装配之前,设置实例化之前的回调函数。通常用于抑制特定目标bean的默认实例化,例如,创建具有特殊TargetSources(池化目标,延迟初始化目标等)的代理,或者实现其他注入策略,例如字段注入。注意:这个接口是一个专用接口,主要用于框架内的内部使用。 建议尽可能实现简单的BeanPostProcessor接口,或者从InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter派生,以便屏蔽此接口的扩展。
postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法,在目标bean实例化之前创建bean,如果在这里创建了bean,则不会走默认的实例化过程,通常用来创建代理。注意工厂方法生成的bean不会走这个方法。
postProcessAfterInstantiation方法,在目标bean实例化后,但是没有进行属性填充前执行的方法。
postProcessPropertyValues方法,在将给定属性值设置到到给定的bean后,对其进行后处理。 允许检查所有的依赖关系是否被满足,例如基于bean属性设置器上的“Required”注解。还允许替换要应用的属性值,通常通过创建基于原始PropertyValues的新MutablePropertyValues实例,添加或删除特定值。
接口应用
这个接口spring不建议用户直接实现,如果必须在这些扩展点应用自己的回调函数,spring建议继承InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter,重写相应的方法即可。
org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.BeanNameAutoProxyCreator,基于beanName创建代理,就是应用了这个接口,在生成bean前生成代理bean,从而替代默认的实例化。
BeanPostProcessor接口
接口描述
/**
* Factory hook that allows for custom modification of new bean instances,
* e.g. checking for marker interfaces or wrapping them with proxies.
*
* <p>ApplicationContexts can autodetect BeanPostProcessor beans in their
* bean definitions and apply them to any beans subsequently created.
* Plain bean factories allow for programmatic registration of post-processors,
* applying to all beans created through this factory.
*
* <p>Typically, post-processors that populate beans via marker interfaces
* or the like will implement {@link #postProcessBeforeInitialization},
* while post-processors that wrap beans with proxies will normally
* implement {@link #postProcessAfterInitialization}.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 10.10.2003
* @see InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
* @see DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor
* @see ConfigurableBeanFactory#addBeanPostProcessor
* @see BeanFactoryPostProcessor
*/
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
*/
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean
* instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The
* post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created
* objects or both through corresponding {@code bean instanceof FactoryBean} checks.
* <p>This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a
* {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method,
* in contrast to all other BeanPostProcessor callbacks.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean
*/
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
}这个接口,允许自定义修改新的bean实例,例如检查标记接口或用代理包装,注意,如果有相互依赖的bean,这里可能无法使用代理。
postProcessBeforeInitialization方法,在任何bean初始化回调(如InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet或自定义init方法)之前,将此BeanPostProcessor应用于给定的新的bean实例。 这个bean已经被填充了属性值。 返回的bean实例可能是原始的包装器。
postProcessAfterInitialization方法,在Bean初始化回调(如InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet或自定义init方法)之后,将此BeanPostProcessor应用于给定的新bean实例。 这个bean已经被填充了属性值。 返回的bean实例可能是原始的包装器。这个方法也会在InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法生成对象后再次不让他生成对象(具体可以参考Spring生成bean的过程)。
接口应用
org.springframework.context.support.ApplicationContextAwareProcessor就是在bean初始化回调之前,注入应用上下文的。
其他扩展点
InitializingBean接口
在执行完BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法后,如果这个bean实现了InitializingBean接口,则会去调用afterPropertiesSet方法。
各种Aware
在在执行完BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法前,如果bean实现了BeanNameAware或BeanClassLoaderAware或BeanFactoryAware,则会调用接口相关的方法,入参就是这个bean关心的值。
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor,作用是在一个bean初始化之前,如果这个bean有Aware接口,实现了EnvironmentAware,EmbeddedValueResolverAware,ResourceLoaderAware,ApplicationEventPublisherAware,MessageSourceAware,ApplicationContextAware相关接口,就通过这些aware的相关接口将上下文设置进去,上述接口除了EmbeddedValueResolverAware接口ClassPathXmlApplicationContext没有实现,其他都实现了,也就是说,调用这些接口的方法入参都是ClassPathXmlApplicationContext就可以了。EmbeddedValueResolverAware的入参是EmbeddedValueResolver,它的构造函数入参是上下文中的beanFactory。
BeanDefinition入口扩展
在定义bean时,可以指定构造函数,设置属性,还可以设置init-method和destroy-method。构造函数不用说,设置属性是在InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#PostProcessPropertyValues方法后执行的,init-method是在InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet方法后执行的,而destroy-method是在容器关闭是被调用的。
扩展点在spring中的注入
前三小节我们了解了很多扩展点,那这些扩展点中的接口是怎么在spring中生效的呢,换句话说在什么时候被调用或被添加到BeanFactory中等待调用呢?
容器级别
我们得从上下文的抽象类AbstractApplicationContext#refresh方法讲起。
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
// 设置上下文启动时间和活跃标记,同时加载属性资源。
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 停掉之前启动的beanFactory如果有的话,同时新生成一个beanFactory,加载配置中的BeanDefinition。
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// 给beanFactory设置类加载器,添加后置处理器`ApplicationContextAwareProcessor`等等。
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)方法就是第一小节提到的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor的调用。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法的调用逻辑:
如果beanFactory是BeanDefinitionRegistry的实现类
拿到入参所有的BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口实现类,挑选出实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的实现类先执行postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法。
接下来调用beanFactory中实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的实现类中实现PriorityOrdered接口的实现类,调用这些实现类前先根据PriorityOrdered的getOrder方法进行排序,然后再按顺序调用postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法。
接下来再调用beanFactory中实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的实现类中实现了Ordered接口的类,也是按顺序调用postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法。
最后调用beanFactory中其他的实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的实现类的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法。
最后的最后,先调用入参中所有实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的实现类的postProcessBeanFactory方法,再调用入参中实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的实现类的postProcessBeanFactory方法。
如果不是则只把入参中的BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现类全部调用一遍。
上边都做完了,接着从beanFactory中获取实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的bean(没有被执行过),也是分为三类,PriorityOrdered组优先调用,Ordered其次,其他垫底。
最终清除beanFactory的metaData缓存(主要是清除类与beanname的映射缓存)
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory)方法就是第二小节中BeanPostProcessor接口实现类的注册。
registerBeanPostProcessors方法的调用逻辑:
先添加BeanPostProcessorChecker。
然后把beanFactory中实现BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类分成四个部分分别添加到beanFactory。
PriorityOrdered部分,实现了PriorityOrdered接口且并不属于MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor的
Ordered部分,实现了Ordered接口且并不属于MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor的
其他的不属于MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor的
属于MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor的
其中PriorityOrdered和Ordered部分先排序,然后按上边的顺序分别加入到beanFactory的beanPostProcessors属性中
bean级别
其余的bean上的接口属性之类的,都是在bean的生成中逐个调用的。
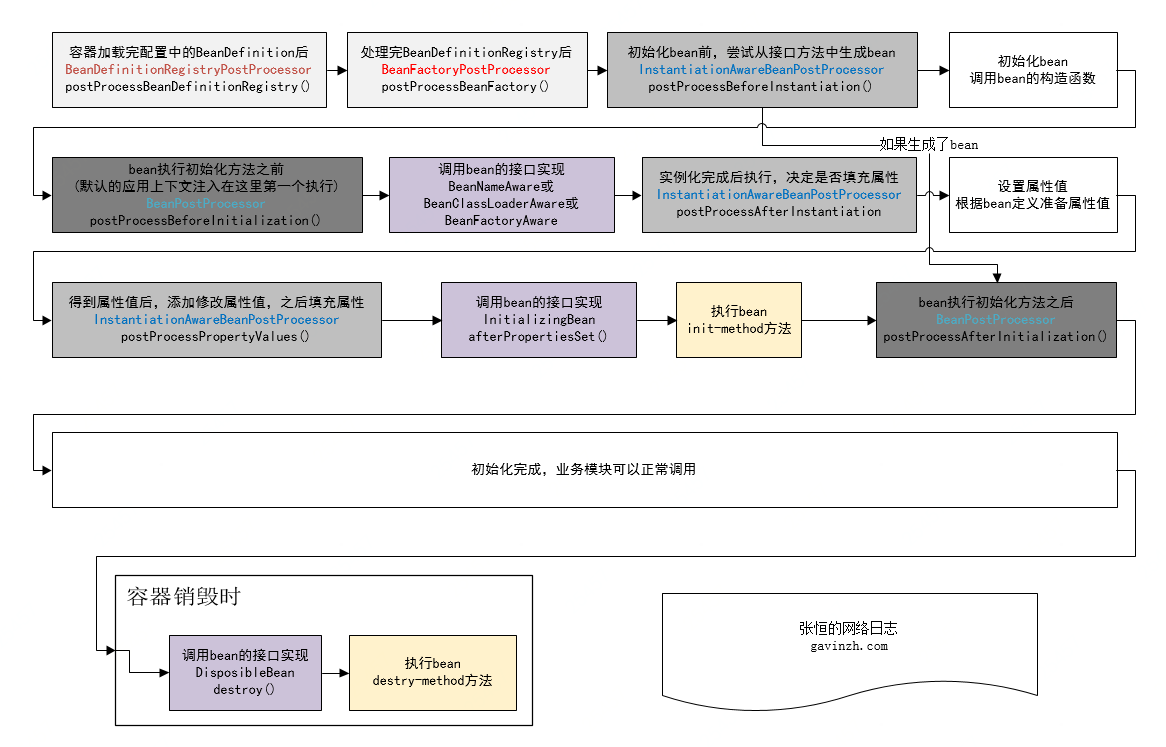
小节
下面由一张图来总结一下扩展点之间的调用顺序。